Searching
B403: Introduction to Algorithm Design and Analysis
Red-Black Trees
| color | key | left | right | p |
Red-black properties:
- Every node is either red or black
- The root is black
- Every leaf (NIL) is black
- If a node is red, then both its children are black
- For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes
Red-Black Tree Example
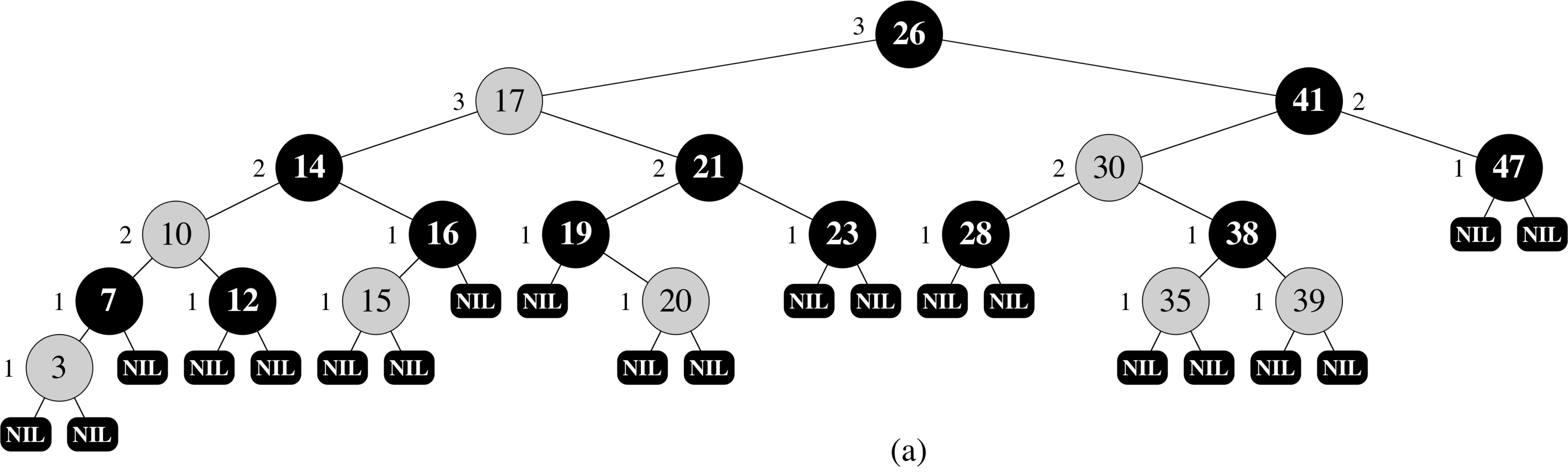
Red-Black Tree Example (internal)
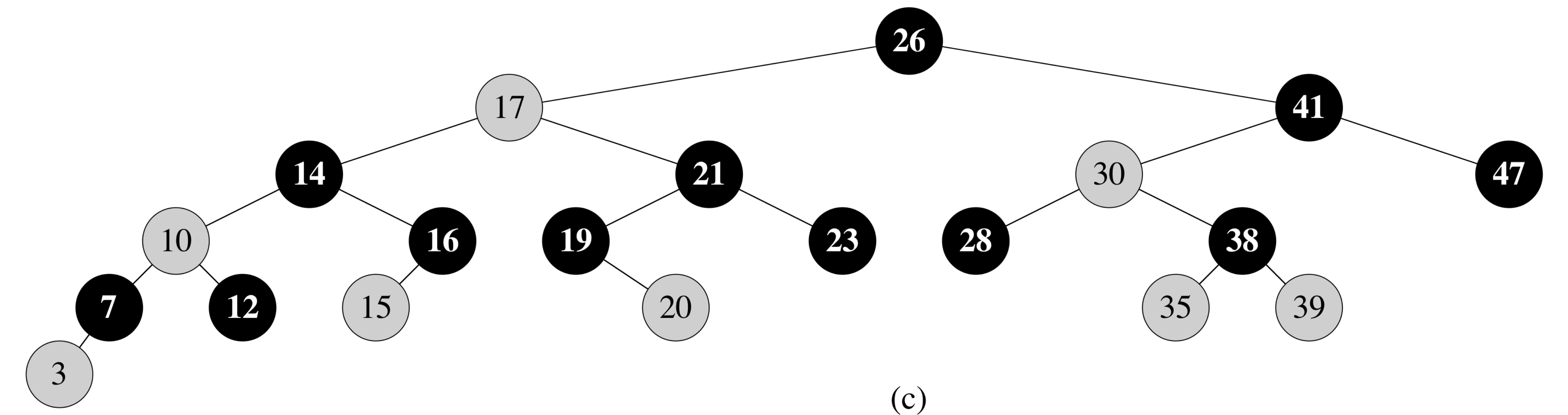
Red-Black Tree Example (simplified)
Limiting the Height of Red-Black Trees
Lemma: A red-black tree with n internal nodes has height at most 2⋅log(n+1)
Definiton: The black-height of a node x, denoted bh(x), is the number of black nodes on any simple path from, but not including, x down to a leaf.
Proof outline:
- First show that the subtree rooted at any node x contains at least 2bh(x)−1 nodes, by induction on the height of x
- Finish the proof by noting that at least half the nodes on any path from the root to a leaf must be black
Exercises
- The longest simple path from a node x in a red-black tree to a descendant leaf has length at most twice that of the shortest simple path from node x to a descendant leaf.
- What is the largest possible number of internal nodes in a red-black tree with black-height k? What is the smallest possible number?
Rotations

Does the search tree property continue to be satisfied after a rotation?
Can a rotation change the height of the tree?
Left-Rotate
Left-Rotate (T, x)
1 y = x.right // set x
2 x.right = y.left // turn y's subtree into x's right subtree
3 if y.left ≠ T.nil
4 y.left.p = x
5 y.p = x.p // link x's parent to y
6 if x.p == T.nil
7 T.root = y
8 elseif x == x.p.left
9 x.p.left = y
10 else x.p.right = y
11 y.left = x // put x on y's left
12 x.p = y

Rotations Example

Tree-Insert
Tree-Insert (T, z)
1 y = NIL
2 x = T.root
3 while x ≠ NIL
4 y = x
5 if z.key ≤ x.key
6 x = x.left
7 else x = x.right
8 z.p = y
9 if y == NIL
10 T.root = z
11 elseif z.key < y.key
12 y.left = z
13 else y.right = z
Tree Insert Example

RB-Insert
RB-Insert (T, z) 1 y = T.nil 2 x = T.root 3 while x ≠ T.nil 4 y = x 5 if z.key ≤ x.key 6 x = x.left 7 else x = x.right 8 z.p = y 9 if y == T.nil 10 T.root = z 11 elseif z.key < y.key 12 y.left = z 13 else y.right = z 14 z.left = T.nil 15 z.right = T.nil 16 z.color = RED 17 RB-Insert-Fixup(T, z) |
Tree-Insert (T, z)
1 y = NIL
2 x = T.root
3 while x ≠ NIL
4 y = x
5 if z.key ≤ x.key
6 x = x.left
7 else x = x.right
8 z.p = y
9 if y == NIL
10 T.root = z
11 elseif z.key < y.key
12 y.left = z
13 else y.right = z
|
RB-Insert-Fixup
RB-Insert-Fixup (T, z) 1 while z.p.color == RED 2 if z.p == z.p.p.left 3 y = z.p.p.right 4 if y.color == RED 5 z.p.color = BLACK // case 1 6 y.color = BLACK // case 1 7 z.p.p.color = RED // case 1 8 z = z.p.p // case 1 9 else if z == z.p.right 10 z = z.p // case 2 11 Left-Rotate(T, z) // case 2 12 z.p.color = BLACK // case 3 13 z.p.p.color = RED // case 3 14 Right-Rotate(T, z.p.p) // case 3 15 else (same as then clause with “right” and “left” exchanged) 16 T.root.color = BLACK
Insert Fixup Example
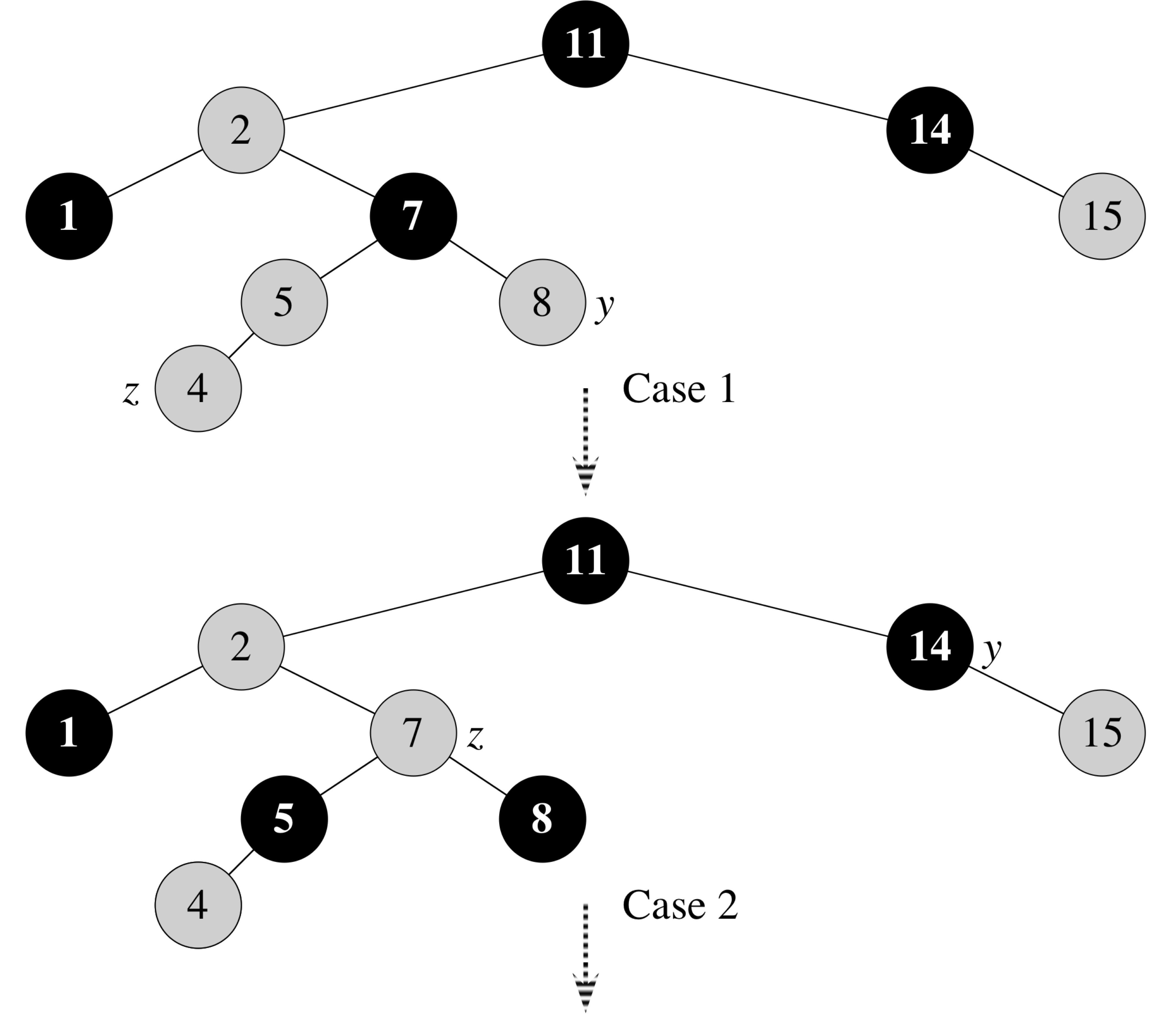
Insert Fixup Example
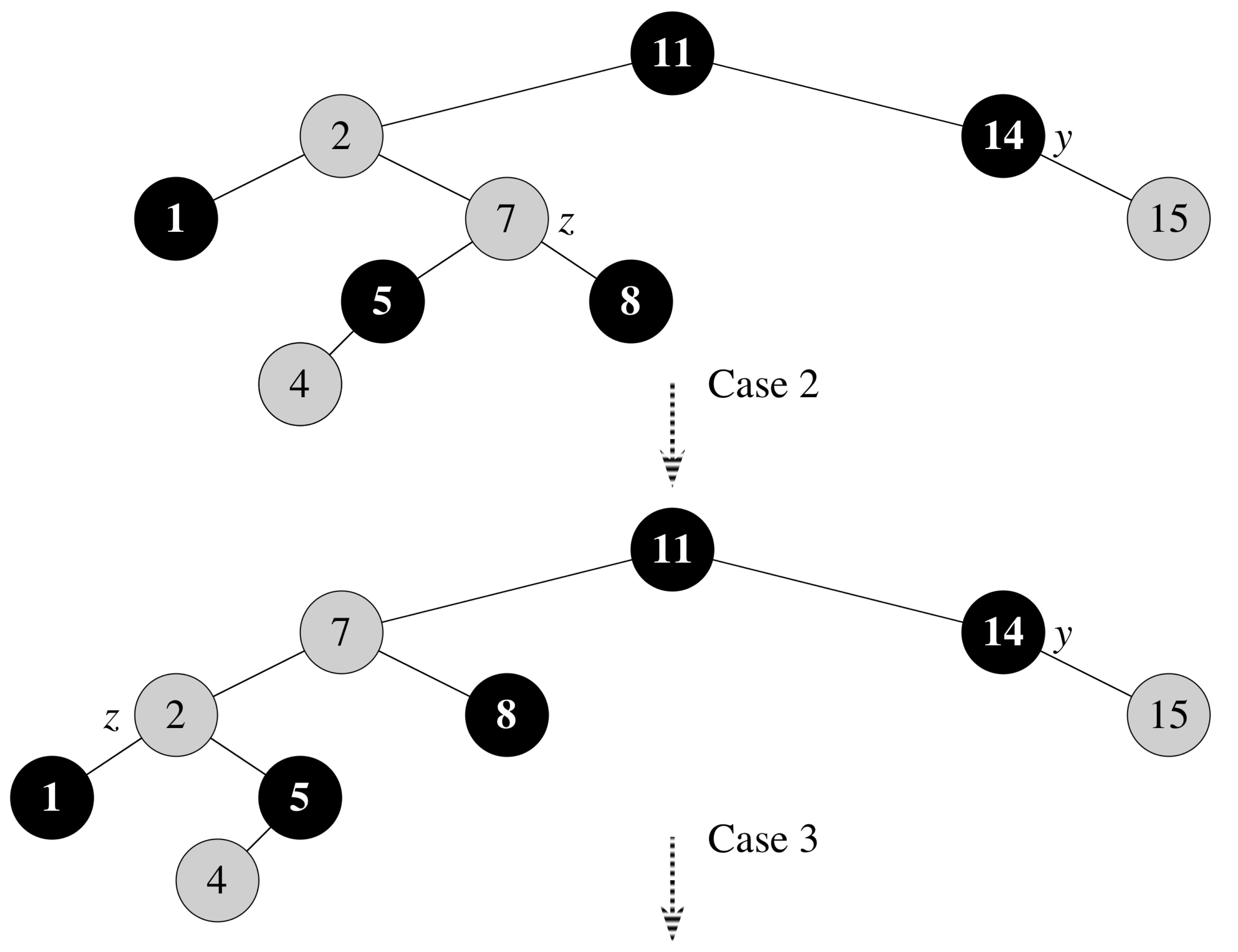
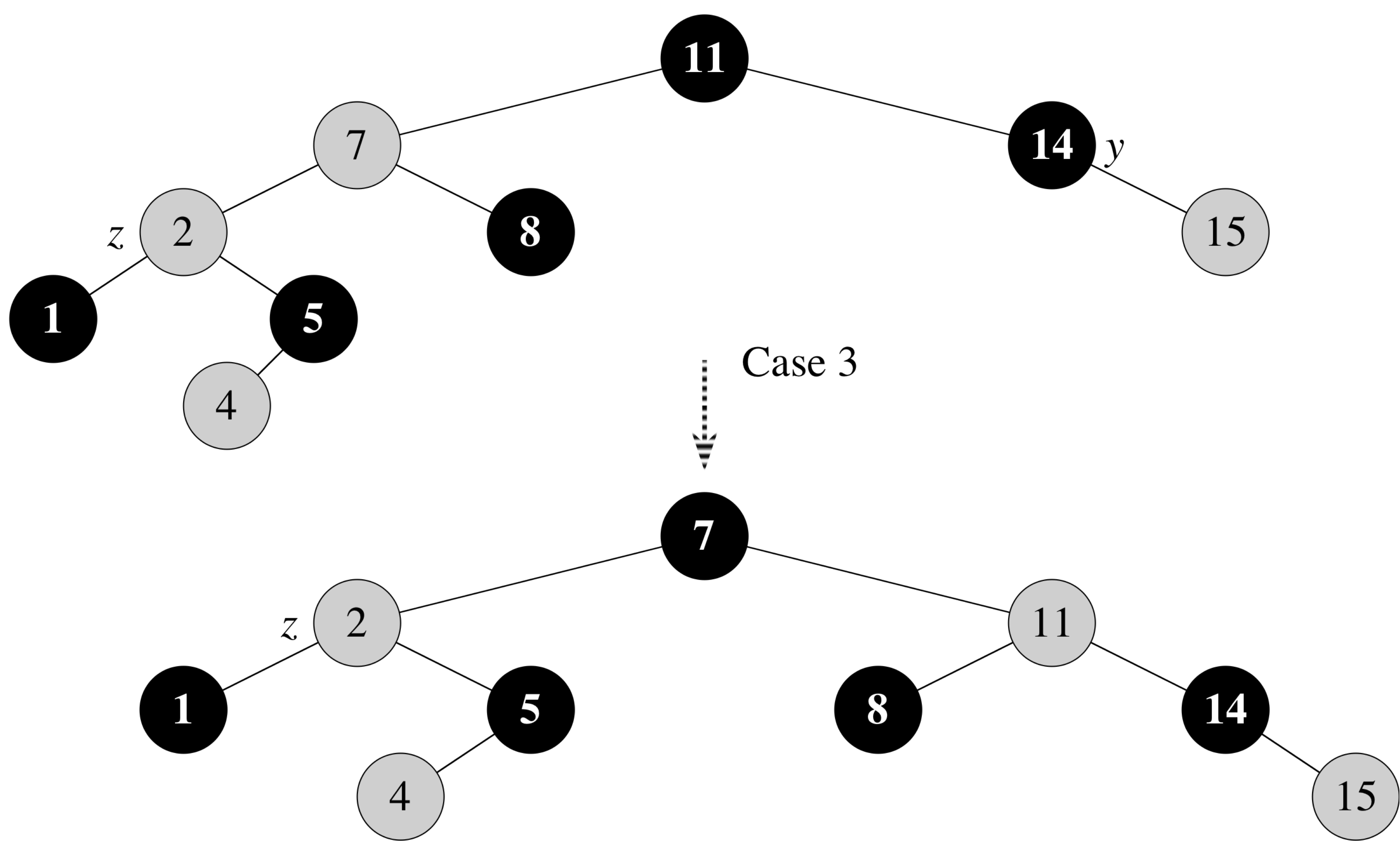
Insert Fixup Example
How does it Work?
Following invariants are satisfied:
- Node z is red
- If z.p is the root, then z.p is black
-
If the tree violates any of the red-black properties, then it violates at most one of them, and the
violation is either of property 2 or property 4
- if the tree violates property 2, it is because z is the root and is red
- If the tree violates property 4, it is because both z and z.p are red
Insert Fixup (Case 1)
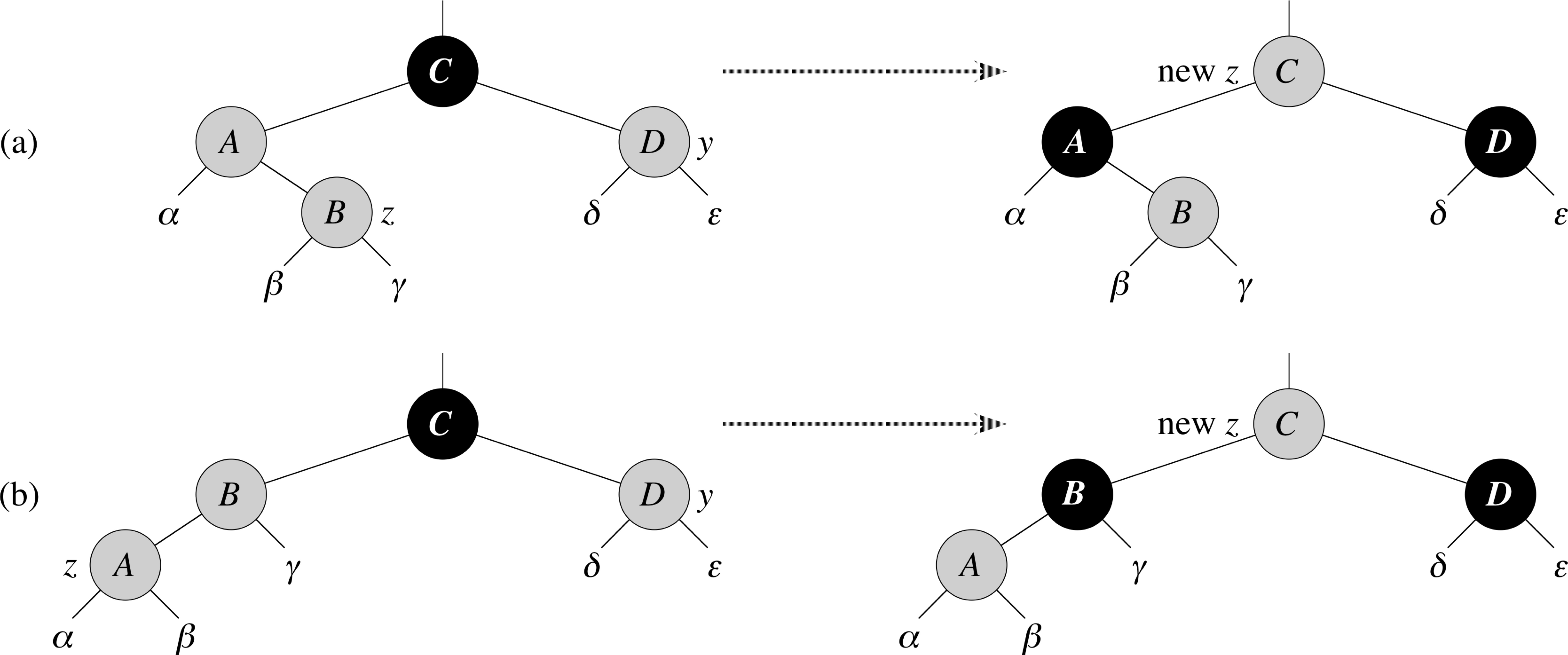
Insert Fixup (Cases 2 and 3)

Deletion from Search Tree
Transplant (T, dst, src)
1 if dst.p == NIL
2 T.root = src
3 elseif dst == dst.p.left
4 dst.p.left = src
5 else dst.p.right = src
6 if src ≠ NIL
7 src.p = dst.p
|
Tree-Delete (T, z) 1 if z.left == NIL 2 Transplant(T, z, z.right) 3 elseif z.right == NIL 4 Transplant(T, z, z.left) 5 else y = Tree-Minimum(z.right) 6 if y.p ≠ z 7 Transplant(T, y, y.right) 8 y.right = z.right 9 y.right.p = y 10 Transplant(T, z, y) 11 y.left = z.left 12 y.left.p = y |
Delete (Cases 1 and 2)


Delete (Case 3)
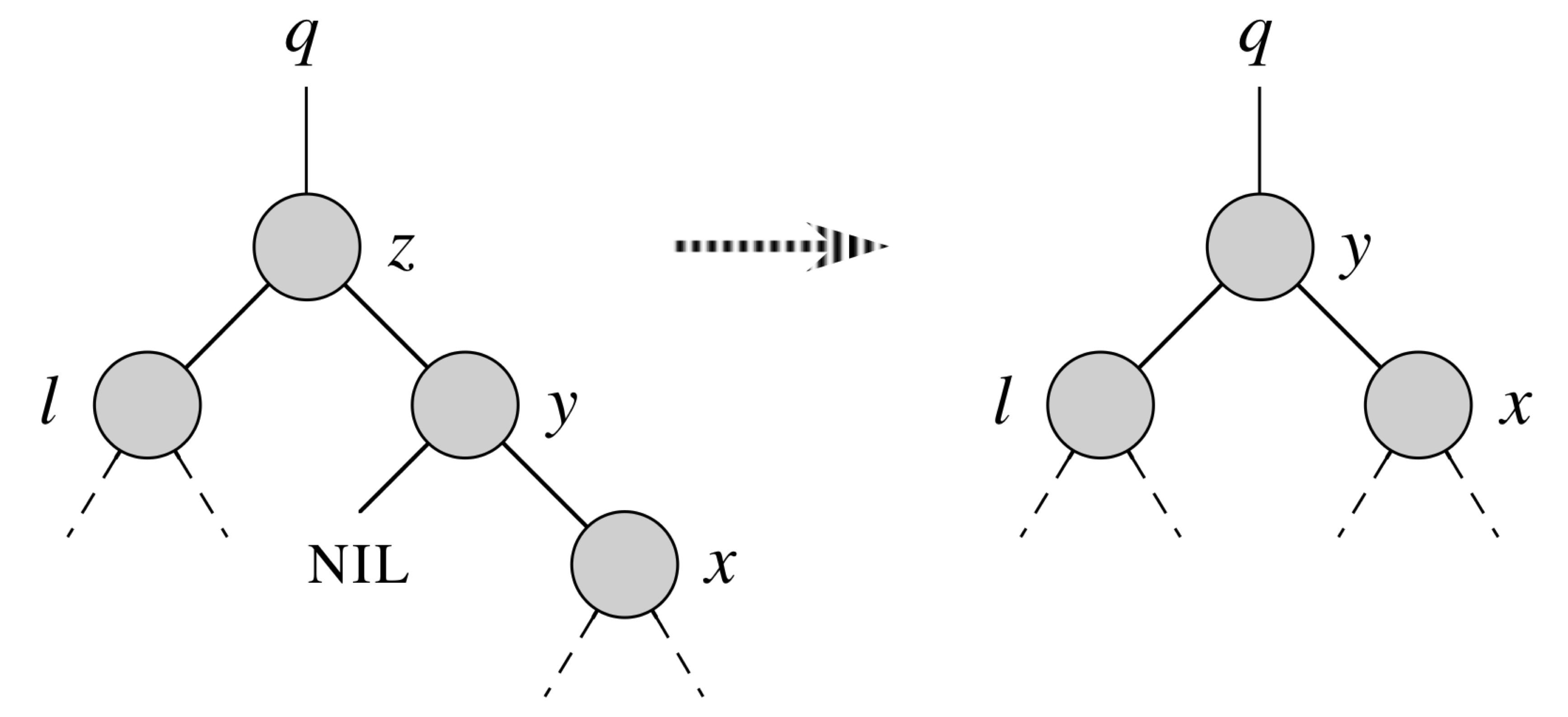
Delete (Case 4)

RB-Translplant
RB-Transplant (T, dst, src)
1 if dst.p == T.nil
2 T.root = src
3 elseif dst == dst.p.left
4 dst.p.left = src
5 else dst.p.right = src
7 src.p = dst.p
|
Transplant (T, dst, src)
1 if dst.p == NIL
2 T.root = src
3 elseif dst == dst.p.left
4 dst.p.left = src
5 else dst.p.right = src
6 if src ≠ NIL
7 src.p = dst.p
|
Deletion from Red-Black Search Tree
RB-Delete (T, z) 1 y = z 2 y-original-color = y.color 3 if z.left == T.nil 4 x = z.right 5 RB-Transplant(T, z, z.right) 6 elseif z.right == T.nil 7 x = z.left 8 RB-Translplant(T, z, z.left) 9 else y = Tree-Minimum(z.right) 10 y-original-color = y.color 11 x = r.right 12 if y.p == z 13 x.p = y 14 else RB-Transplant(T, y, y.right) 15 y.right = z.right 16 y.right.p = y 17 RB-Transplant(T, z, y) 18 y.left = z.left 19 y.left.p = y 20 y.color = z.color 21 if y-original-color == BLACK 22 RB-Delete-Fixup(T, x) |
Tree-Delete (T, z) 1 if z.left == NIL 2 Transplant(T, z, z.right) 3 elseif z.right == NIL 4 Transplant(T, z, z.left) 5 else y = Tree-Minimum(z.right) 6 if y.p ≠ z 7 Transplant(T, y, y.right) 8 y.right = z.right 9 y.right.p = y 10 Transplant(T, z, y) 11 y.left = z.left 12 y.left.p = y |
RB-Delete-Fixup
RB-Delete-Fixup (T, x)
1 while x ≠ T.root and x.color == BLACK
2 if x == x.p.left
3 w = x.p.right
4 if w.color == RED
5-8 // CASE 1
9 if w.left.color == BLACK and w.right.color == BLACK
10-11 // CASE 2
12 else if w.right.color == BLACK
13-16 // CASE 3
17-21 // CASE 4
22 else (same as then clause with “right” and “left” exchanged)
23 x.color = BLACK
RB-Delete-Fixup: Case 1
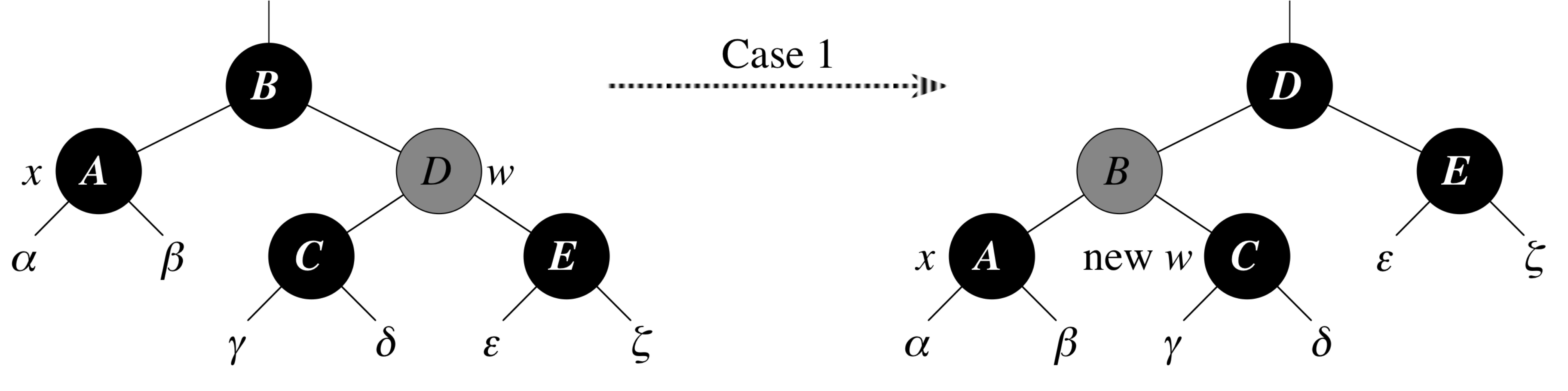
x's sibling w is red
RB-Delete-Fixup: Case 2
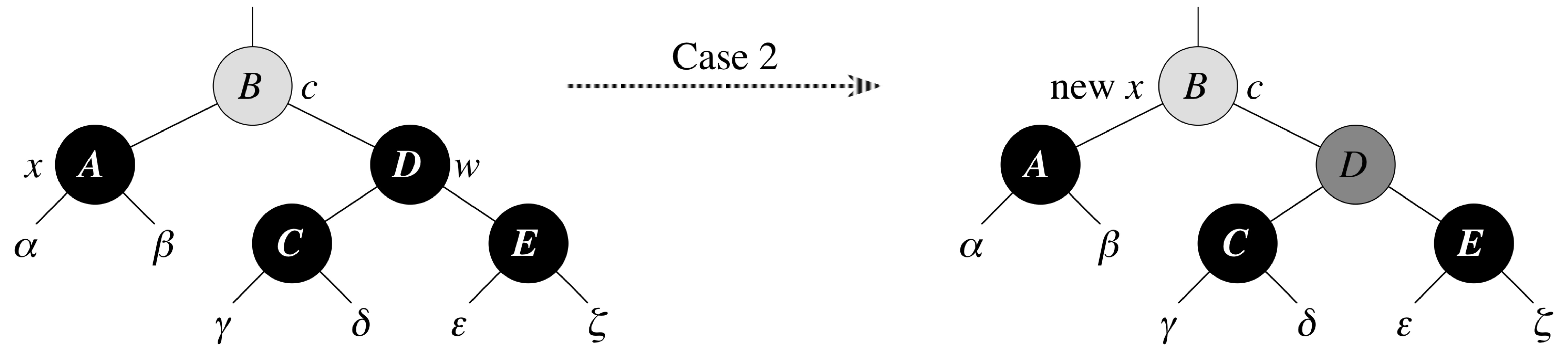
x's sibling w is black and both of w's children are black
RB-Delete-Fixup: Case 3
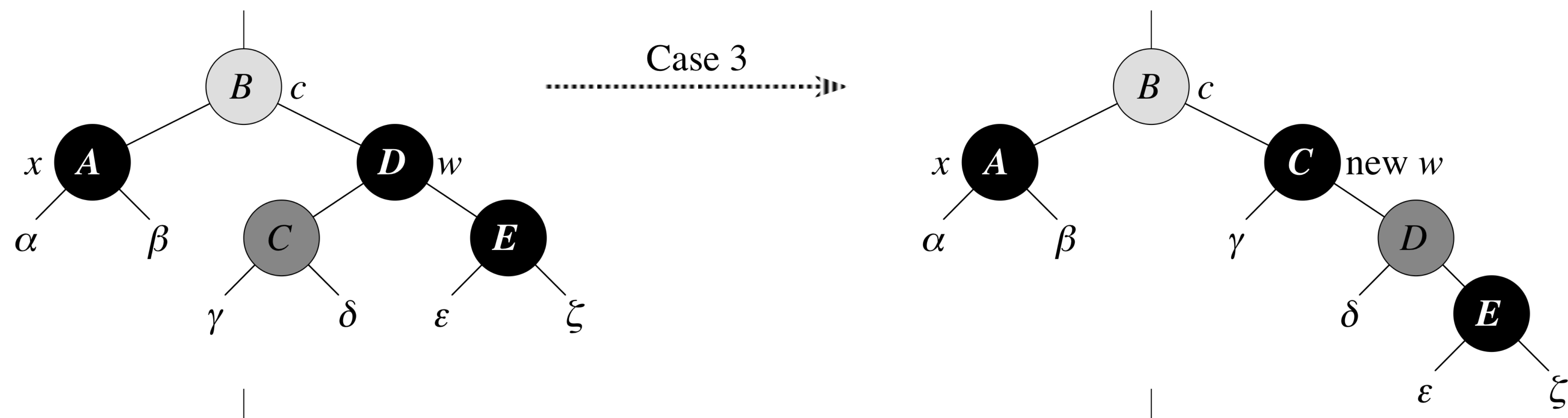
x's sibling w is black, w's left child is red, and w's right child is black
RB-Delete-Fixup: Case 4
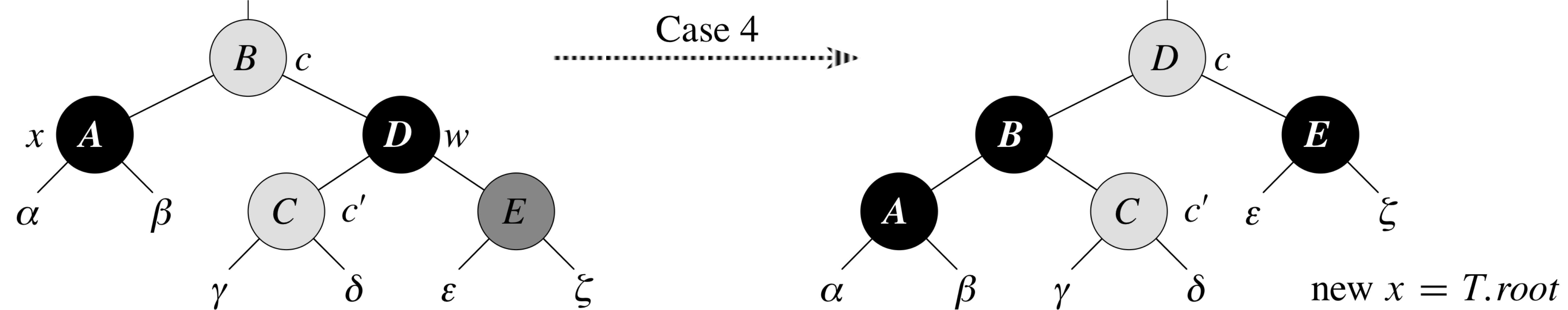
x's sibling w is black, w's left right is red
Augmenting Red-Black Trees
- Dynamic order statistics
- quick order statistics in a dynamic list
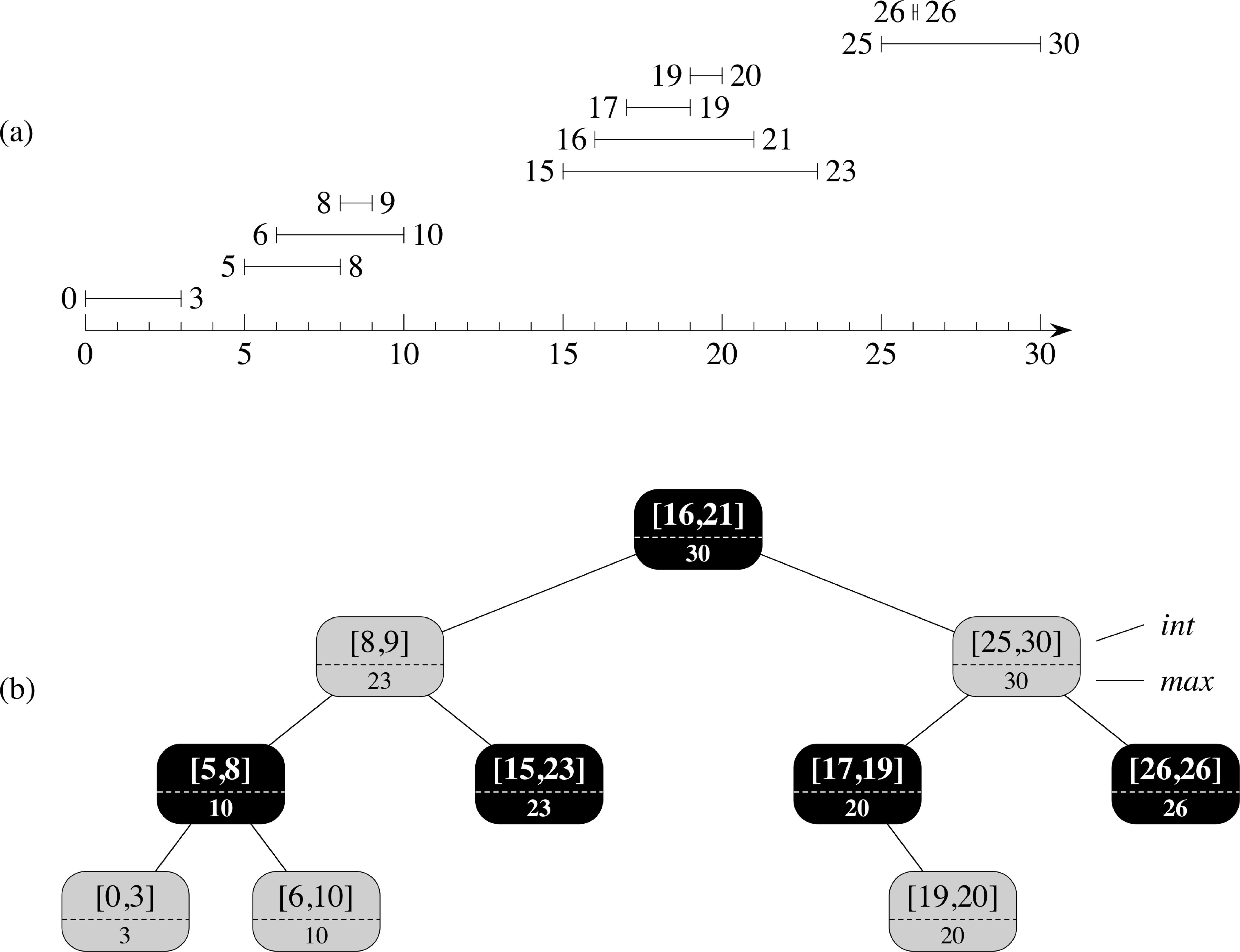
- Interval Trees
- quickly determining conflicting intervals
Where might you use interval trees?
Dynamic Order Statistic
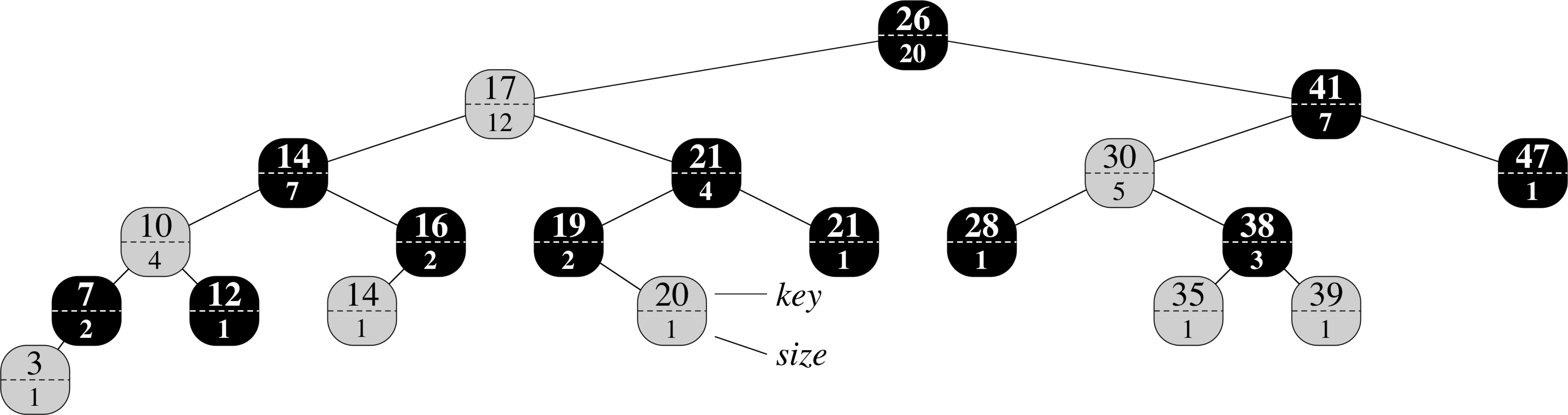
Dynamic Order Statistic: Tree Update

Interval Trees